
hhlee
2024-11-12 21:55:20
Behind
Defending Against DDoS with AWS WAF: Focusing on User Experience
🗞️
[Update] AI Sticker Icon Generation Feature
The AI sticker image generation feature is now live! You can now create the perfect sticker images to match any context, whether you're feeling quirky, creative...
![[Update] AI Sticker Icon Generation Feature](https://cdn.videostew.com/files/thumb/5b07ea0af-7ueeitewk)
🗞️
[Update] Sharper Images & Vanishing Backgrounds: Image Upscaling & BG-Removal Just Leveled Up! ✨
File Editor just leveled up—say hello to sharper upscales and cleaner background removal.Open any image in your library, hit “File Editor,” and watch your still...
![[Update] Sharper Images & Vanishing Backgrounds: Image Upscaling & BG-Removal Just Leveled Up! ✨](https://cdn.videostew.com/files/thumb/5344bad0c-7u7f8x3g9)
🎓
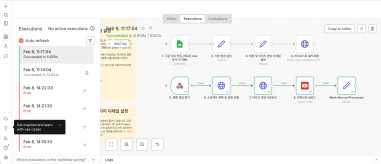
Just paste a news link and watch YouTube Shorts upload itself! (Videostew API & n8n combo guide)
Hey there! 🎬 In this post we’re wiring up Videostew with the no-code ninja n8n so you can paste a news URL, grab a coffee, and watch the magic: video rendered ➜...
📖
Whip Up ‘Econ-101’ Reels in a Flash—With AI-Generated Images on the Side 🤑✨
When you're whipping up a video, which step eats up the most time?Scripting is tough, sure—but the real buzzkill is often the image hunt. You know the feeling: ...
🗞️
[Update] Whip Up AI Images in One Click—Now in Wizard Mode! 🪄
Wizard Mode just leveled up: you can now summon fresh AI images in the same flow. 🪄Flip the switch in the final detailed-settings step of Wizard Mode—set Visual...
![[Update] Whip Up AI Images in One Click—Now in Wizard Mode! 🪄](https://cdn.videostew.com/files/thumb/b336facab-7u4jpk3cp)
📖
Ring in 2026 Lunar New Year with a snazzy video greeting template—no firecrackers required! 🧧
Hey there! 🐉 2026 is charging in on a fiery red horse, and Lunar New Year is almost here. From everyone at Videostew, may your year overflow with good fortune, ...
📣
Small-Biz Marketing in One Word: Video—How to Automate It Like a Pro with Videostew API
Meet Hi-3D: the startup that’s been turning corporate daydreams into 3D-printed prototypes. These days, though, they’ve gone full sci-fi—leveraging AI-driven ma...
🤔
In the Age When Video-Making Got Easy, Direction Is the New Superpower 🎬✨
Videostew just made a cameo on YouTube’s “Laughing Class”! 🎬Getting name-dropped alongside rock stars like Grock and ChatGPT? We’ll take it. But the real win wa...

Running a website inevitably means facing abnormal traffic attacks. Especially when aiming for global services, the domain itself becomes more exposed, increasing the likelihood of becoming a target.
To ensure safe website operations, Videostew uses AWS WAF. Before accessing Videostew, you must first pass through the gatekeeper called WAF. After that, Videostew itself employs several mechanisms to verify and filter out incorrect requests.
< Traces of brute force attacks that sneak in as effortlessly as breathing >
Attack patterns are varied, and we defend against various types through numerous settings. In this post, however, we'll focus solely on the indiscriminate DDoS attacks.
DDoS Attack
A DDoS attack is a method of sending multiple requests simultaneously to cause server downtime. The downtime itself is critical, but it can also be exploited for additional attacks through unexpected error messages or settings caused by server overflow.
Several reasons make DDoS attacks challenging to prevent:
At Videostew, we have a two-tier defense setup to block DDoS attacks while minimizing user inconvenience. It's structured with a non-bypassable Stage 1 block with loose conditions, and a bypassable Stage 2 block with sensitive conditions.
WAF's Rate Limit Blocking (Stage 1)
The very first step is to filter out large volumes of traffic at the WAF level. If attack requests reach the actual web server, the burden of verification increases, so it's best to cut off the attack at the WAF.
The issue, as mentioned earlier, is that once a request is blocked at the WAF, it's difficult to handle afterward. Since access itself is blocked at the source, if legitimate customer traffic is mistakenly blocked, it can be somewhat challenging to rectify. Therefore, we set slightly looser criteria (judging that it's truly, truly abnormal traffic).
The number of requests accepted within a specified time is added through [Rules > Add rules > Add my own rules and rule groups].
The important thing is the Rate-limiting criteria, and there is no one-size-fits-all answer. This is because access patterns differ for each service. You can set it tightly and relax it if unintended blocks occur, or approach it the other way around. The time can also be set freely, but if you set it to 5 minutes, you need to increase the Rate Limit accordingly (since legitimate traffic shouldn't be blocked), which means the impact window for a malicious attacker is also extended.
The point here is that the settings are kept very loose. The purpose of this setting is not to block all DDoS attacks, but to initially filter out only the excessively heavy traffic.
Backend & WAF CAPTCHA (Step 2)
This second stage is where malicious attacks and high-traffic users ambiguously mix. A tighter criterion than the first one should be applied (since filtering is still necessary), and at the same time, a means to request removal should be provided since they might be legitimate users.
The setup is simple. Manage a blacklist of IPs using the IP Sets feature on WAF, and instead of blocking the IPs on this blacklist, offer a CAPTCHA feature.
In the backend code, if a user from a specific IP connects excessively within a minute, triggers multiple CSRF errors, repeatedly fails form validations, or continuously requests non-existent pages, the IP is dynamically added to the IP Sets using the WAF SDK.
When this happens, the user encounters Amazon's awkwardly designed CAPTCHA. Until they pass this, the WAF will not allow them to reach the web server. If the user proves they are human, an `aws-waf-token` cookie is created, allowing them access to the web server. As long as this cookie is valid, the user can normally use the service again.
However, the user is still on the blacklist IP. This means that if the allowed token cookie expires or is lost, the CAPTCHA will appear again. Therefore, when a user with an `aws-waf-token` accesses, they are encouraged to "request to unblock the IP" once more through guidance.
< Mistaken for an attack IP but confirmed as human, here's your disassembly guide >
After clicking the guide message, you can verify your humanity once more using Google CAPTCHA. Once verified, an API request will be triggered using the AWS SDK to remove the respective IP.
On the frontend, display the "Manual Disassembly Request" guide message only to users with `aws-waf-token` and without `aws-waf-verified`.
Effect
This is a graph of actual DDoS traffic. DDoS attacks show such spikes because they flood traffic from various IPs at specific times. You can see that a significant portion is filtered out by the set rules. However, some unfiltered traffic still escapes... Tightening the first condition could inconvenience regular users, so enhancing the second condition adjusted in the backend seems necessary.
And More...
Here, we only covered CAPTCHA blocking using WAF's Rate Limit Rule and IP Sets. Our team also uses AWS Managed Rules (blocking methods provided by Amazon). There's no one-size-fits-all in WAF settings, so we believe that customizing it gradually as you apply it to your service is the best approach.